Abstract
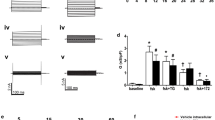
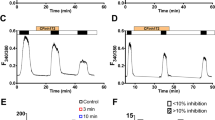
Calcium-dependent potassium channels are implicated in electrolyte transport, cell volume regulation and mechanical responses in epithelia, although the pathways for calcium entry and their coupling to the activation of potassium channels are not fully understood. We now show molecular evidence for the presence of TRPV4, a calcium permeable channel sensitive to osmotic and mechanical stress, and its functional coupling to the large conductance calcium-dependent potassium channel (BKCa) in a human bronchial epithelial cell line (HBE). Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction, intracellular calcium imaging and whole-cell patch–clamp experiments using HBE cells demonstrated the presence of TRPV4 messenger and Ca2+ entry, and outwardly rectifying cationic currents elicited by the TRPV4 specific activator 4α-phorbol 12,13-didecanoate (4αPDD). Cell-attached and whole-cell patch–clamp of HBE cells exposed to 4αPDD, and hypotonic and high-viscosity solutions (related to mechanical stress) revealed the activation of BKCa channels subsequent to extracellular Ca2+ influx via TRPV4, an effect lost upon antisense-mediated knock-down of TRPV4. Further analysis of BKCa modulation after TRPV4 activation showed that the Ca2+ signal can be generated away from the BKCa location at the plasma membrane, and it is not mediated by intracellular Ca2+ release via ryanodine receptors. Finally, we have shown that, unlike the reported disengagement of TRPV4 and BKCa in response to hypotonic solutions, cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelial cells (CFBE) preserve the functional coupling of TRPV4 and BKCa in response to high-viscous solutions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade YN, Fernandes J, Vazquez E, Fernandez-Fernandez JM, Arniges M, Sanchez TM, Villalon M, Valverde MA (2005) TRPV4 channel is involved in the coupling of fluid viscosity changes to epithelial ciliary activity. J Cell Biol 168:869–874
Arniges M, Fernandez-Fernandez JM, Albrecht N, Schaefer M, Valverde MA (2006) Human TRPV4 channel splice variants revealed a key role of ankyrin domains in multimerization and trafficking. J Biol Chem 281:1580–1586
Arniges M, Vazquez E, Fernandez-Fernandez JM, Valverde MA (2004) Swelling-activated Ca2+ entry via TRPV4 channel is defective in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. J Biol Chem 279:54062–54068
Christensen AP, Corey DP (2007) TRP channels in mechanosensation: direct or indirect activation? Nat Rev Neurosci 8:510–521
Cotton CU (2000) Basolateral potassium channels and epithelial ion transport. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 23(3):270–272
Cozens AL, Yezzi MJ, Kunzelmann K, Ohrui T, Chin L, Eng K, Finkbeiner WE, Widdicombe JH, Gruenert DC (1994) CFTR expression and chloride secretion in polarized immortal human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 10:38–47
Davis KA, Cowley EA (2006) Two-pore-domain potassium channels support anion secretion from human airway Calu-3 epithelial cells. Pflugers Arch 451:631–641
Earley S, Heppner TJ, Nelson MT, Brayden JE (2005) TRPV4 forms a novel Ca2+ signaling complex with ryanodine receptors and BKCa channels. Circ Res 97:1270–1279
Feranchak AP, Doctor RB, Troetsch M, Brookman K, Johnson SM, Fitz JG (2004) Calcium-dependent regulation of secretion in biliary epithelial cells: the role of apamin-sensitive SK channels. Gastroenterology 127:903–913
Fernandes J, Lorenzo IM, Andrade YN, Garcia-Elias A, Serra SA, Fernandez-Fernandez JM, Valverde MA (2008) IP3 sensitizes TRPV4 channel to the mechano- and osmotransducing messenger 5′-6′-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid. J Cell Biol 181:143–155
Fernandez-Fernandez JM, Nobles M, Currid A, Vazquez E, Valverde MA (2002) Maxi K+ channel mediates regulatory volume decrease response in a human bronchial epithelial cell line. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283:C1705–C1714
Giraldez F, Valverde MA, Sepulveda FV (1988) Hypotonicity increases apical membrane Cl− conductance in Necturus enterocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 942:353–356
Gruenert DC, Willems M, Cassiman JJ, Frizzell RA (2004) Established cell lines used in cystic fibrosis research. J Cyst Fibros 3(Suppl 2):191–196
Harteneck C, Reiter B (2007) TRP channels activated by extracellular hypo-osmoticity in epithelia. Biochem Soc Trans 35:91–95
Hoffmann EK, Dunham PB (1995) Membrane mechanisms and intracellular signalling in cell volume regulation. Int Rev Cytol 161:173–262
Hoyer J, Distler A, Haase W, Gogelein H (1994) Ca2+ influx through stretch-activated cation channels activates maxi K+ channels in porcine endocardial endothelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:2367–2371
Jayaraman S, Joo NS, Reitz B, Wine JJ, Verkman AS (2001) Submucosal gland secretions in airways from cystic fibrosis patients have normal [Na+] and pH but elevated viscosity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:8119–8123
Jespersen T, Grunnet M, Olesen SP (2005) The KCNQ1 potassium channel: from gene to physiological function. Physiology 20:408–416
Johnson NT, Villalon M, Royce FH, Hard R, Verdugo P (1991) Autoregulation of beat frequency in respiratory ciliated cells. Demonstration by viscous loading. Am Rev Respir Dis 144:1091–1094
Liedtke W, Kim C (2005) Functionality of the TRPV subfamily of TRP ion channels: add mechano-TRP and osmo-TRP to the lexicon!. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:2985–3001
Lock H, Valverde MA (2000) Contribution of the IsK (MinK) potassium channel subunit to regulatory volume decrease in murine tracheal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 275:34849–34852
MacLeod RJ, Lembessis P, Hamilton JR (1992) Differences in Ca2+-mediation of hypotonic and Na+-nutrient regulatory volume decrease in suspensions of jejunal enterocytes. J Membr Biol 130:23–31
Montell C (2005) The TRP superfamily of cation channels. Sci STKE 2005:re3
Pasantes-Morales H, Morales-Mulia S (2000) Influence of calcium on regulatory volume decrease: role of potassium channels. Nephron 86:414–427
Rutland J, Cole PJ (1981) Nasal mucociliary clearance and ciliary beat frequency in cystic fibrosis compared with sinusitis and bronchiectasis. Thorax 36:654–658
Sachs F, Morris CE (1998) Mechanosensitive ion channels in nonspecialized cells. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 132:1–77
Salathe M (2006) Regulation of mammalian ciliary beating. Annu Rev Physiol 69:401–422
Sanderson MJ, Dirksen ER (1986) Mechanosensitivity of cultured ciliated cells from the mammalian respiratory tract: implications for the regulation of mucociliary transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 83:7302–7306
Sardini A, Amey JS, Weylandt KH, Nobles M, Valverde MA, Higgins CF (2003) Cell volume regulation and swelling-activated chloride channels. Biochim Biophys Acta 1618:153–162
Satir P, Sleigh MA (1990) The physiology of cilia and mucociliary interactions. Annu Rev Physiol 52:137–155
Schultz SG, Dubinsky WP, Lapointe JY (1998) Volume regulation and ‘cross-talk’ in sodium-absorbing epithelial cells. Contrib Nephrol 123:205–219
Schwiebert EM, Benos DJ, Egan M, Stutts MJ, Guggino WB (1999) CFTR is a conductance regulator as well as a chloride channel. Physiol Rev 79:S145–S166
Sheppard DN, Giraldez F, Sepulveda FV (1988) Kinetics of voltage- and Ca2+ activation and Ba2+ blockade of a large-conductance K+ channel from Necturus enterocytes. J Membr Biol 105:65–75
Sheppard DN, Valverde MA, Giraldez F, Sepulveda FV (1991) Potassium currents of isolated Necturus enterocytes: a whole-cell patch-clamp study. J Physiol 433:663–676
Shuttleworth TJ (1999) What drives calcium entry during [Ca2+]i oscillations? challenging the capacitative model. Cell Calcium 25:237–246
Sienaert I, Huyghe S, Parys JB, Malfait M, Kunzelmann K, De SH, Verleden GM, Missiaen L (1998) ATP-induced Ca2+ signals in bronchial epithelial cells. Pflugers Arch 436:40–48
Spungin B, Silberberg A (1984) Stimulation of mucus secretion, ciliary activity, and transport in frog palate epithelium. Am J Physiol 247:C299–C308
Strotmann R, Harteneck C, Nunnenmacher K, Schultz G, Plant TD (2000) OTRPC4, a nonselective cation channel that confers sensitivity to extracellular osmolarity. Nat Cell Biol 2:695–702
Tuvia S, Almagor A, Bitler A, Levin S, Korenstein R, Yedgar S (1997) Cell membrane fluctuations are regulated by medium macroviscosity: evidence for a metabolic driving force. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:5045–5049
Valverde MA (1999) CIC channels: leaving the dark ages on the verge of a new millennium. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11:509–516
Valverde MA, Mintenig GM, Sepulveda FV (1993) Differential effects of tamoxifen and I- on three distinguishable chloride currents in T84 intestinal cells. Pflugers Arch 425:552–554
Valverde MA, O’Brien JA, Sepulveda FV, Ratcliff RA, Evans MJ, College WH (1995) Impaired cell volume regulation in intestinal crypt epithelia of cystic fibrosis mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:9038–9041
Valverde MA, Vazquez E, Munoz FJ, Nobles M, Delaney SJ, Wainwright BJ, Colledge WH, Sheppard DN (2000) Murine CFTR channel and its role in regulatory volume decrease of small intestine crypts. Cell Physiol Biochem 10:321–328
Vazquez E, Nobles M, Valverde MA (2001) Defective regulatory volume decrease in human cystic fibrosis tracheal cells because of altered regulation of intermediate conductance Ca2+- dependent potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:5329–5334
Vriens J, Watanabe H, Janssens A, Droogmans G, Voets T, Nilius B (2004) Cell swelling, heat, and chemical agonists use distinct pathways for the activation of the cation channel TRPV4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:396–401
Warth R (2003) Potassium channels in epithelial transport. Pflugers Arch 446:505–513
Warth R, Hamm K, Bleich M, Kunzelmann K, von Hahn T, Schreiber R, Ullrich E, Mengel M, Trautmann N, Kindle P, Schwab A, Greger R (1999) Molecular and functional characterization of the small Ca2+-regulated K+ channel (rSK4) of colonic crypts. Pflugers Arch 438:437–444
Watanabe H, Davis JB, Smart D, Jerman JC, Smith GD, Hayes P, Vriens J, Cairns W, Wissenbach U, Prenen J, Flockerzi V, Droogmans G, Benham CD, Nilius B (2002) Activation of TRPV4 channels (hVRL-2/mTRP12) by phorbol derivatives. J Biol Chem 277:13569–13577
Watanabe H, Vriens J, Janssens A, Wondergem R, Droogmans G, Nilius B (2003) Modulation of TRPV4 gating by intra- and extracellular Ca2+. Cell Calcium 33:489–495
Winters SL, Davis CW, Boucher RC (2007) Mechanosensitivity of mouse tracheal ciliary beat frequency: roles for Ca2+, purinergic signaling, tonicity, and viscosity. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 292:L614–L624
Yule DI, Gallacher DV (1988) Oscillations of cytosolic calcium in single pancreatic acinar cells stimulated by acetylcholine. FEBS Lett 239:358–362
Zham JM, Gaillard D, Dupuit F, Hinnrasky J, Dorin JR, Puchelle E (1997) Early alterations in airway mucociliary clearance and inflammation of the lamina propria in CF mice. Am J Physiol 272:C853–C859
Acknowledgment
We thank D. C. Gruenert (San Francisco, USA) for the gift of the cell lines. Work funded by the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science (SAF2006-04973 to M.A.V. and SAF2006-13893-C02-02 to J.M.F.-F.), Ministry of Health (Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria, red HERACLES RD06/0009 to M.A.V.), Generalitat de Catalunya (SGR05-266 to M.A.V.), and Fundació la Marató de TV3 (061331 to J.M.F.-F.). J.M.F.-F. is a Ramón y Cajal Fellow. The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
José M. Fernández-Fernández and Yaniré N. Andrade contributed equally to this work, and both should be considered first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández-Fernández, J.M., Andrade, Y.N., Arniges, M. et al. Functional coupling of TRPV4 cationic channel and large conductance, calcium-dependent potassium channel in human bronchial epithelial cell lines. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 457, 149–159 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0516-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0516-3